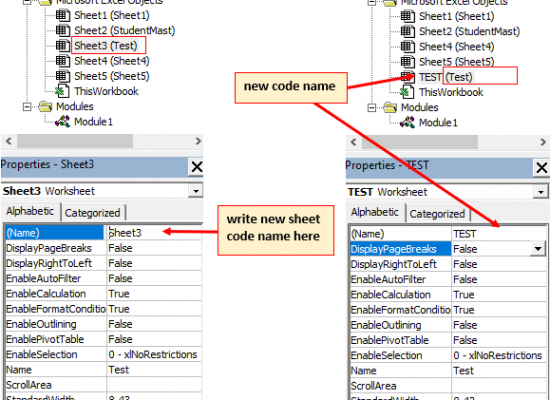
Worksheet index name, tab name and code name
In Excel VBA we can refer a worksheet by three ways.
1. Index name – It represents at which position from left to right a given worksheet is present. Left most worksheet has 1 index. In the below image “Sheet1” has 1 index, “StudentMast” has 2 indext and so on. A given woksheet index can be changed. If “Sheet1” is shifted to right most position then it will have index of 5.
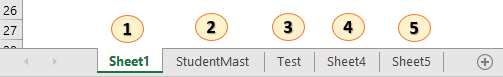
2. Tab name – It represents name of a worksheet in Excel user interface. In the above image “Sheet1”, “StudentMast”, “Test” are worksheets tab names.
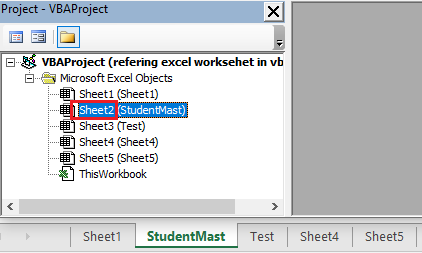
3. Code name – Worksheet code name can only be seen in VBA IDE. Press ALT +F11 to open VBA IDE. In VBA IDE worksheet naming format is CodeName (TabName). In the below image “Sheet1” tab name has Sheet1 code name, “StudentMast” tab name has Sheet2 code name.
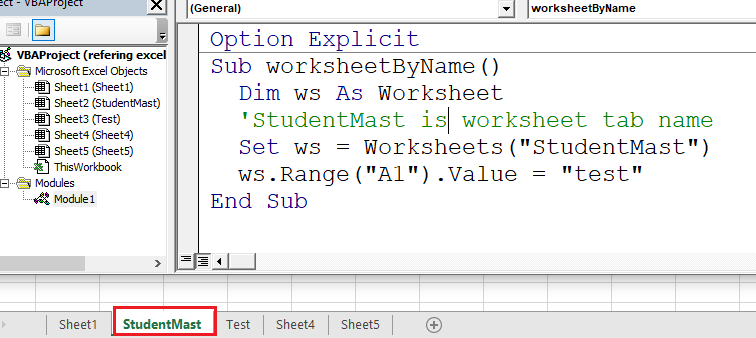
VBA to refer worksheet using worksheet name
The below image represents code for referring worksheet by tab name if worksheet present in the same workbook.
Above can be alternatively written as
Sub worksheetByName2()
'StudentMast is worksheet tab name
Worksheets("StudentMast").Range("A1").Value = "test"
End SubNow if you want to refer worksheet of differenct workbook then below is the code.
Sub worksheetByName3()
Dim wrkBk As Workbook
Set wrkBk = Workbooks("myWorkbook.xlsb")
'TestSht is worksheet tab name
wrkBk.Worksheets("TestSht").Range("A1").Value = "test"
End SubIn the above code “myWorkbook.xlsb” is workbook name and “TestSht” is worksheet present in “myWorkbook.xlsb” workbook. Above code is written in workbook other than “myWorkbook.xlsb”.
VBA to refer worksheet using worksheet index number

Sub worksheetByIdex()
Dim ws As Worksheet
'StudentMast is at 2 number from left
Set ws = Worksheets(2) ''refers StudentMast sheet
MsgBox ws.Name
End SubIn the above code Worksheets(2) means 2nd worksheet from left which is “StudentMast” worksheet. MsgBox ws.Name will display name of 2nd worksheet.
VBA to refer worksheet using worksheet code name

Sub worksheetBySheetCodeName()
Dim ws As Worksheet
'Sheet2 is code name of StudentMast worksheet
Set ws = Sheet2 ''refers StudentMast sheet
MsgBox ws.Name
End SubIn the above Sub MsgBox ws.Name line will display StudentMast in message box.
VBA to refer worksheet of other workbook using worksheet code name
One can directly refer by the code name of a worksheet of a workbook in which code resides.
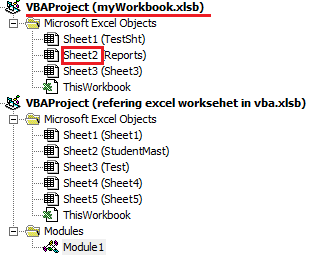
In the below image if you want refer Sheet2 code name of myWorkbook.xlsb workbook by writing code in other workbook then Workbooks(“myWorkbook.xlsb”).Sheet2 will not work.
Function getShtObj(wrkbkNm As String, shtCdNm As String) As Worksheet
'wrkbkNm is workbook name with extension
'shtCdNm is worksehet code name
Dim wrkBk As Workbook, sht As Worksheet
Set wrkBk = Workbooks(wrkbkNm)
For Each sht In wrkBk.Worksheets
If sht.CodeName = shtCdNm Then
Set getShtObj = sht
Exit For
End If
Next sht
End FunctionSub worksheetBySheetCodeName2()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = getShtObj("myWorkbook.xlsb", "Sheet2")
MsgBox ws.Name
End SubNow in the above code section which is written in other workbook not in myWorkbook , function getShtObj is used to get worksheet object by inputting workbook name and worksheet code name.
Sub worksheetBySheetCodeName2 calls getShtObj function. Now MsgBox ws.Name line will show Reports in message box which is worksheet present in myWorkbook workbook.
Changing worksheet code name or module name in VBA IDE
Default code name of a worksheet can be changed. Select worksheet in VBA IDE then press F4 function key to bring properties window or go to View tab then click on Properties window. In (Name) fill you can change code name of selected sheet.
Advantages of changing worksheet code name or module name
- One can give sensible user-friendly name thus increasing code readability
- One directly transfer module into other workbook without worrying about sheet code name conflict.
Note:- Do not change worksheet code name after writing code, otherwise code lines which refers this worksheet by code name will give error. Change sheet code name first then write code lines which refers this sheet.
Best practices for referring worksheet
Referring a project worksheet by code name is more preferable over worksheet tab name or worksheet index. But sometimes one may require to refer using worksheet tab name or worksheet index.
VBA code snippets related to worksheet
Where to test or run these code snippets?
To test or run these code snippets follow the below steps.
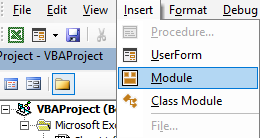
Press ALT+F11 to open VBA IDE.
Click on the Insert tab then click on Module to create a Standard Module.
Double click on newly created module to bring coding area of that module
Now if given code snippet is not wrapped between sub and end sub then copy paste below code in module then copy paste code snippet between sub and End Sub. In the below code you can write any name at place of test.
Sub test()
End SubIf already wrapped between sub and end sub then directly copy code and paste it in module.
To run a Sub or Subroutine or Procedure place mouse cursor anywhere between sub and end sub then press function key F5.
VBA Code snippets
In most code lines worksheet code name is used but one can also refer by worksheet tab name or index number.
Refer active worksheet or current worksheet sheet VBA
Dim asht As Worksheet
Set asht = ActiveSheet
MsgBox asht.Name
'OR
MsgBox ActiveSheet.NameCount total worksheets in a workbook VBA
Worksheets.CountVBA to refer first sheet or leftmost worksheet of a workbook
Dim fstSht As Worksheet
Set fstSht = Worksheets(1)
MsgBox fstSht.NameVBA to refer last sheet or rightmost worksheet of a workbook
Dim lastSht As Worksheet
Set lastSht = Worksheets(Worksheets.Count)
MsgBox lastSht.NameVBA to refer right and left worksheet of a particular worksheet
'right worksheet of Sheet2 code name
Dim rSht As Worksheet
Set rSht = Sheet2.Next
MsgBox rSht.Name
'OR
Dim rSht As Worksheet
Set rSht = Worksheets(Sheet2.Index + 1)
MsgBox rSht.Name
'left worksheet of Sheet2 code name
Dim lSht As Worksheet
Set lSht = Sheet2.Previous
MsgBox lSht.Name
'OR
Dim lSht As Worksheet
Set lSht = Worksheets(Sheet2.Index - 1)
MsgBox lSht.NameVBA to create and delete a worksheet
'create worksheet
Worksheets.Add
'delete worksheet sheet3 is code name of worksheet
Sheet3.DeleteVBA to change worksheet tab name
'changing tab name of Sheet6
Sheet6.Name = "Tracking"
'changing tab name of active sheet
ActiveSheet.Name = "ABC"VBA to change worksheet tab color
'Sheet6 is code name of a worksheet
'using predefined color constant
Sheet6.Tab.Color = vbRed
'OR
'using color number
Sheet6.Tab.Color = 255
'OR
'using color index (1 to 56)
Sheet6.Tab.ColorIndex = 3
'OR
'using RGB (red,green,blue) color values
Sheet6.Tab.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)VBA to activate a particular worksheet
'using code name
Sheet6.Activate
'OR
'using worksheet tab name
Worksheets("Test").ActivateVBA to copy and move a worksheet in a new workbook
'sheet3 is code name
'sheet3 will get copied in the new workbook
Sheet3.CopyVBA to protect all worksheets using password
Sub protectAllWSheets()
Dim pw As String
Dim wSht As Worksheet
pw = "123" 'here you can change password
For Each wSht In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
wSht.Protect Password:=pw
Next wSht
End SubVBA to unprotect all worksheets using password
Sub unprotectAllWSheets()
Dim pw As String
Dim wSht As Worksheet
pw = "123" 'here you can change password
For Each wSht In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
wSht.Unprotect Password:=pw
Next wSht
End SubVBA to make worksheet hidden, extrahidden and visible
xlSheetHidden sheets can be made visible in Excel user interface by right clicking mouse on a sheet and selecting unhide.
xlSheetVeryHidden sheets are not shown in unhide worksheets list. Veryhidden sheet can only be made visible using VBA or VBA IDE.
'*make sure workbook is unprotected
'makes sheet hidden
Sheet3.Visible = xlSheetHidden
'makes sheet veryhidden
Sheet3.Visible = xlSheetVeryHidden
'makes sheet visible
Sheet3.Visible = xlSheetVisibleVBA to sort worksheets/sheets in ascending and descending order
Excel VBA to sort sheets in descending (Z to A) order
Sub shortSheetNamesDescOrder()
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Dim shtNm As String, shtCnt As Integer
Dim i As Integer, j As Integer
shtCnt = Sheets.Count
For i = 1 To shtCnt - 1
shtNm = LCase(Sheets(i).Name)
For j = i + 1 To shtCnt
If LCase(Sheets(j).Name) > shtNm Then
Sheets(j).Move before:=Sheets(i)
End If
Next j
Next i
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End SubExcel VBA to sort sheets in ascending (A to Z) order
Sub shortSheetNamesAscOrder()
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Dim shtNm As String, shtCnt As Integer
Dim i As Integer, j As Integer
shtCnt = Sheets.Count
For i = 1 To shtCnt - 1
shtNm = LCase(Sheets(i).Name)
For j = i + 1 To shtCnt
If LCase(Sheets(j).Name) < shtNm Then
Sheets(j).Move before:=Sheets(i)
End If
Next j
Next i
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End SubVBA to auto color all worksheet or sheets tabs
The below code uses random color indexes ranging from 1 to 56. In this method color range is limited to 56 colors.
Sub ColorSheetTabs_v1()
'only from 56 predefined colors
'using random color index number
Dim shtCnt As Integer, i As Integer
Dim clrIdx As Byte
shtCnt = Sheets.Count
For i = 1 To shtCnt
clrIdx = CByte(55 * Rnd() + 1)
Sheets(i).Tab.ColorIndex = clrIdx
Next i
End SubThe below code uses a random RGB color mix. In this method color range is unlimited.
Sub ColorSheetTabs_v2()
'range of color is unlimited
'using random RGB number
Dim shtCnt As Integer, i As Integer
Dim r As Byte, g As Byte, b As Byte
shtCnt = Sheets.Count
For i = 1 To shtCnt
r = CByte(254 * Rnd()) 'red color
g = CByte(254 * Rnd()) 'green color
b = CByte(254 * Rnd()) 'blue color
Sheets(i).Tab.Color = RGB(r, g, b)
Next i
End SubVBA to create all worksheets hyperlink list (Hyperlink Menu of Worksheets)
Sub sheetsHyperlinkList()
Dim shtCnt As Integer, inCel As Range
Dim hypListWSht As Worksheet, shtNm As String
Dim i As Integer, j As Integer
Set hypListWSht = Worksheets.Add(before:=Sheets(1))
hypListWSht.Name = "HyperlinkList"
shtCnt = Sheets.Count
j = 0
For i = 2 To shtCnt
Set inCel = hypListWSht.Range("A1").Offset(j)
shtNm = Sheets(i).Name
inCel.Hyperlinks.Add anchor:=inCel, Address:="", _
SubAddress:="'" & shtNm & "'!A1", TextToDisplay:=shtNm
j = j + 1
Next i
End Sub